# About load balancing
Moleculer has several built-in load balancing strategies.
If a Service has multiple running instances,
ServiceRegistry uses these strategies to select a node from all available nodes.
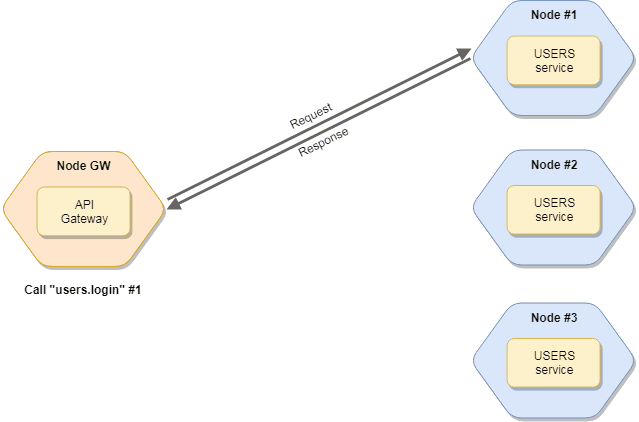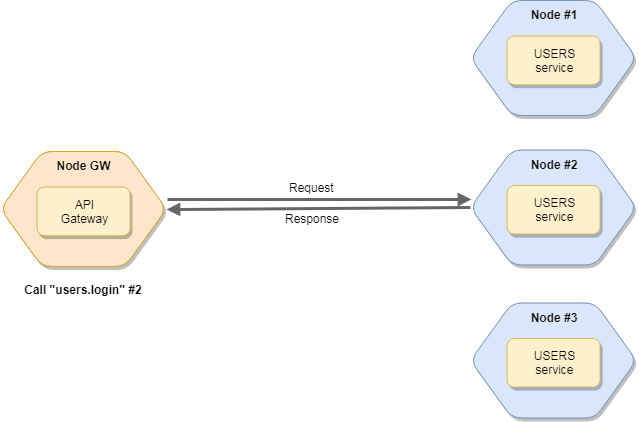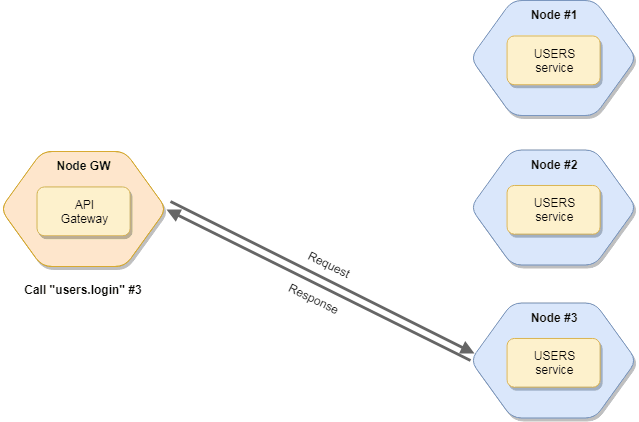
The default (pre-set) invocation mode is the RoundRobinStrategy.
# Built-in Strategies
To configure Strategy, set "strategy()" builder option when creating the ServiceBroker.
Alternatively, set up the Strategy of the ServiceBrokerConfig using the "setStrategyFactory()" method.
Configure a balancing Strategy
// Create a "StrategyFactory"
StrategyFactory strategy = new XorShiftRandomStrategyFactory();
// Method #1: Setup using ServiceBrokerConfig
ServiceBrokerConfig config = new ServiceBrokerConfig();
config.setStrategyFactory(strategy);
ServiceBroker broker = new ServiceBroker(config);
// Method #2: Setup using ServiceBroker.builder()
ServiceBroker broker = ServiceBroker.builder()
.strategy(strategy)
.build();
# Round-Robin Strategy
This Strategy selects a node based on round-robin algorithm.
This is the default invocation Strategy.
You can use the "setPreferLocal" function to configure ServiceRegistry
to invoke locally available services whenever they are available in the JVM.
If set to "true", ServiceBroker will always use internal Action calls, if possible.
Such a function exists for each StrategyFactory.
Usage
RoundRobinStrategyFactory strategy = new RoundRobinStrategyFactory();
strategy.setPreferLocal(true);
ServiceBroker broker = ServiceBroker.builder().strategy(strategy).build();
# Random Strategies
These strategies randomly select the callable node.
The load on each node (as in round-robin) will be roughly the same.
Usage
// Faster pseudo random
XorShiftRandomStrategyFactory strategy = new XorShiftRandomStrategyFactory();
// Slower secure random
SecureRandomStrategyFactory strategy = new SecureRandomStrategyFactory();
# CPU usage-based Strategy
This Strategy selects a node which has the lowest CPU usage.
Due to the node list can be very long,
it gets samples and selects the node with the lowest CPU usage from only samples instead of the whole node list.
CPU-based load balancing works even when the application is heterogeneous (consisting of Java and Node.js modules).
Usage
// Create CPU monitor
SigarMonitor cpuMonitor = new SigarMonitor();
// Create CPU-based strategy
CpuUsageStrategyFactory invocationStrategy = new CpuUsageStrategyFactory();
invocationStrategy.setLowCpuUsage(5);
invocationStrategy.setMaxTries(3);
// Create service broker
ServiceBroker broker = ServiceBroker.builder()
.strategy(invocationStrategy)
.monitor(cpuMonitor)
.build();
To determine CPU usage, ServiceBroker needs a Monitor instance that can query the current CPU usage.
Such Monitor is the SigarMonitor based on the Sigar API.
It requires the presence of JAR files for the Sigar API in the Java classpath.
It is also necessary to copy the native Sigar binaries into the "java.library.path" directory.
Using the Sigar API is optional; if it not found on the classpath, ServiceBroker will automatically use the JMX-based CPU monitor.
Strategy options
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sampleCount | int | 3 | The number of samples. The minimum value is 1 (you can't turn off sampling). |
| lowCpuUsage | int | 10 | The low CPU usage percent (%). The node which has lower CPU usage than this value is selected immediately. |
# Latency-based Strategy
This Strategy selects a node which has the lowest latency, measured by periodic ping commands.
NetworkLatencyStrategy will ping each node one by one.
Due to slow sampling, it may take a few minutes for the Services to select optimal nodes.
Usage
// Create latency-based strategy
NetworkLatencyStrategyFactory strategy = new NetworkLatencyStrategyFactory();
strategy.setSampleCount(5);
strategy.setCollectCount(10);
strategy.setPingInterval(10);
strategy.setPingTimeout(5000);
// Create service broker
ServiceBroker broker = ServiceBroker.builder().strategy(strategy).build();
Strategy options
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sampleCount | int | 5 | The number of samples. If you have a lot of hosts/nodes, it's recommended to increase the value. Minimum value is "1". |
| collectCount | int | 5 | The number of measured latency per host to keep in order to calculate the average latency. |
| pingInterval | int | 10 | Ping interval in SECONDS. If you have a lot of host/nodes, it's recommended to increase the value. |
| pingTimeout | long | 5000 | Ping timeout time, in MILLISECONDS. |
# Sharding Strategy
Shard invocation Strategy is based on consistent-hashing algorithm.
It uses a key value from context "params" or "meta" to route the request to nodes.
It means that requests with same key value will be routed to the same node.
Usage
Shard key is "name" in context params :
// Create sharding strategy
ShardStrategyFactory strategy = new ShardStrategyFactory();
strategy.setShardKey("name");
// Create service broker
ServiceBroker broker = ServiceBroker.builder().strategy(strategy).build();
Shard key is user.id in context meta :
ShardStrategyFactory strategy = new ShardStrategyFactory();
strategy.setShardKey("#user.id");
ServiceBroker broker = ServiceBroker.builder().strategy(strategy).build();
TIP
If shard key is in context's "meta" it must be declared with a "#" at the beginning. The actual "#" is ignored.
Strategy options
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| shardKey | String | null | Shard key |
| vnodes | int | 10 | Number of virtual nodes |
| ringSize | Integer | null | Size of the ring |
| cacheSize | int | 1024 | Size of the cache |
# Custom Strategy
Custom Strategy can be created by implementing StrategyFactory and Strategy interfaces.
We recommend to copy the source of SecureRandomStrategyFactory
and SecureRandomStrategy
classes, and modify the "next()" method in the "SecureRandomStrategy.java".
Usage
MyCustomStrategyFactory strategy = new MyCustomStrategyFactory();
ServiceBroker broker = ServiceBroker.builder().strategy(strategy).build();